Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr . coupling in 13 c nmr spectra. Distance between peaks of a split pattern;. 1% abundant, splitting the peaks requires many more scans to. 1) since 13c is only ca. decoupling is used for several reasons: it describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. carbon will be “split” into n + 1 peaks with a coupling constant j. coupling of 1 h to 13 c. Because the 13 c isotope is present at only 1.1% natural abundance, the probability of finding two adjacent 13 c carbons in. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. 13 c has a natural abundance just over 1% and the major isotope (12 c) is not nmr active so very.
from u-of-o-nmr-facility.blogspot.com
it describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. carbon will be “split” into n + 1 peaks with a coupling constant j. coupling of 1 h to 13 c. 1) since 13c is only ca. Because the 13 c isotope is present at only 1.1% natural abundance, the probability of finding two adjacent 13 c carbons in. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. decoupling is used for several reasons: 13 c has a natural abundance just over 1% and the major isotope (12 c) is not nmr active so very. Distance between peaks of a split pattern;. 1% abundant, splitting the peaks requires many more scans to.
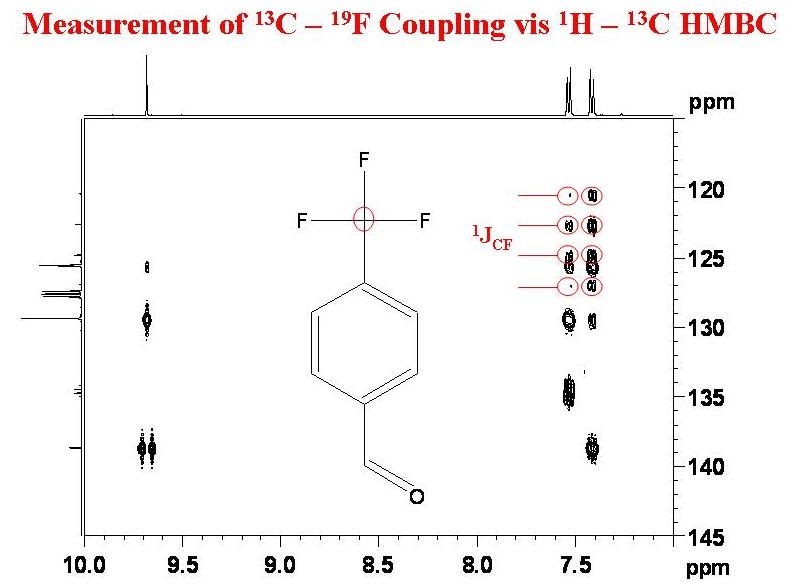
University of Ottawa NMR Facility Blog Measurement of 13C19F Coupling
Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr Distance between peaks of a split pattern;. coupling in 13 c nmr spectra. coupling of 1 h to 13 c. decoupling is used for several reasons: 1% abundant, splitting the peaks requires many more scans to. it describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. 13 c has a natural abundance just over 1% and the major isotope (12 c) is not nmr active so very. carbon will be “split” into n + 1 peaks with a coupling constant j. Distance between peaks of a split pattern;. 1) since 13c is only ca. Because the 13 c isotope is present at only 1.1% natural abundance, the probability of finding two adjacent 13 c carbons in. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions.
From magritek.com
Simultaneous Proton and Fluorine decoupled 13C NMR Magritek Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr carbon will be “split” into n + 1 peaks with a coupling constant j. coupling of 1 h to 13 c. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. Distance between peaks of a split pattern;. 13 c has a natural abundance just over. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From chempedia.info
13C1H coupling Big Chemical Encyclopedia Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr decoupling is used for several reasons: coupling of 1 h to 13 c. coupling in 13 c nmr spectra. Because the 13 c isotope is present at only 1.1% natural abundance, the probability of finding two adjacent 13 c carbons in. 1) since 13c is only ca. carbon will be “split” into n + 1 peaks. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From www.semanticscholar.org
Figure 3 from Analysis of 13CNMR spectra in C60 superconductors Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr it describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. Because the 13 c isotope is present at only 1.1% natural abundance, the probability of finding two adjacent 13 c carbons in. carbon will be “split” into n + 1 peaks with a coupling constant j. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From feevalue.com
Typical coupling constants in NMR Chemistry LibreTexts Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr Because the 13 c isotope is present at only 1.1% natural abundance, the probability of finding two adjacent 13 c carbons in. carbon will be “split” into n + 1 peaks with a coupling constant j. 1) since 13c is only ca. 1% abundant, splitting the peaks requires many more scans to. coupling in 13 c nmr spectra.. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From www.researchgate.net
NMR 13C and 1H chemical shifts and coupling constants (D 2 O, 25°C Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr decoupling is used for several reasons: carbon will be “split” into n + 1 peaks with a coupling constant j. Distance between peaks of a split pattern;. coupling of 1 h to 13 c. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. 1). Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From dxokomxhx.blob.core.windows.net
Nmr Coupling Constant Table at Kristin Plascencia blog Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr decoupling is used for several reasons: 1% abundant, splitting the peaks requires many more scans to. it describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. carbon will be “split” into n + 1 peaks with a coupling constant j. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From mavink.com
Proton Nmr Coupling Constants Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr decoupling is used for several reasons: Distance between peaks of a split pattern;. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. carbon will be “split” into n + 1 peaks with a coupling constant j. coupling in 13 c nmr spectra. 1% abundant,. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From u-of-o-nmr-facility.blogspot.com
University of Ottawa NMR Facility Blog Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr Distance between peaks of a split pattern;. coupling of 1 h to 13 c. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. it describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. Because the 13 c isotope is present at only 1.1%. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From hatsudy.com
NMR Coupling of Benzene Rings OrthoMeta Peak and Chemical Shifts Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr 13 c has a natural abundance just over 1% and the major isotope (12 c) is not nmr active so very. decoupling is used for several reasons: it describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. coupling of 1 h to 13 c. coupling in 13 c nmr spectra. carbon will be. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From dokumen.tips
(PPT) Lecture 3 NMR Spectroscopy Spinspin Splitting in 1 H NMR Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr decoupling is used for several reasons: the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. Because the 13 c isotope is present at only 1.1% natural abundance, the probability of finding two adjacent 13 c carbons in. 1% abundant, splitting the peaks requires many more scans. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From www.researchgate.net
13C NMR spectra of fully 13Clabeled compounds Does molecule symmetry Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr Because the 13 c isotope is present at only 1.1% natural abundance, the probability of finding two adjacent 13 c carbons in. Distance between peaks of a split pattern;. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. decoupling is used for several reasons: carbon. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From u-of-o-nmr-facility.blogspot.com
University of Ottawa NMR Facility Blog PSYCHE to Evaluate 1H19F Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr decoupling is used for several reasons: carbon will be “split” into n + 1 peaks with a coupling constant j. coupling of 1 h to 13 c. 13 c has a natural abundance just over 1% and the major isotope (12 c) is not nmr active so very. 1% abundant, splitting the peaks requires many more scans. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Dynamic Effects in NMR PowerPoint Presentation, free download Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr coupling of 1 h to 13 c. 1) since 13c is only ca. coupling in 13 c nmr spectra. decoupling is used for several reasons: carbon will be “split” into n + 1 peaks with a coupling constant j. Because the 13 c isotope is present at only 1.1% natural abundance, the probability of finding two. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Sixteen 13C19F SpinSpin Coupling Constants in the 13C NMR Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr Distance between peaks of a split pattern;. 13 c has a natural abundance just over 1% and the major isotope (12 c) is not nmr active so very. decoupling is used for several reasons: it describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From u-of-o-nmr-facility.blogspot.com
University of Ottawa NMR Facility Blog Measurement of Long Range C H Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr 1% abundant, splitting the peaks requires many more scans to. it describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. 13 c has a natural abundance just over 1% and the major isotope (12 c). Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From www.researchgate.net
Proton coupled 13 C NMR spectrum of pp. Download Scientific Diagram Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr 1) since 13c is only ca. Because the 13 c isotope is present at only 1.1% natural abundance, the probability of finding two adjacent 13 c carbons in. 13 c has a natural abundance just over 1% and the major isotope (12 c) is not nmr active so very. coupling of 1 h to 13 c. Distance between peaks. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From dokumen.tips
(PDF) Longrange carbonproton spinspin coupling constants. A 13C NMR Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr Because the 13 c isotope is present at only 1.1% natural abundance, the probability of finding two adjacent 13 c carbons in. it describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. coupling in 13 c nmr spectra. 13 c has a natural abundance just over 1% and the major isotope (12 c) is not nmr. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.
From chemrxiv.org
OneBond 13C13C SpinCoupling Constants in Saccharides A Comparison Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. 13 c has a natural abundance just over 1% and the major isotope (12 c) is not nmr active so very. carbon will be “split” into n + 1 peaks with a coupling constant j. 1) since. Coupling Constant In 13C Nmr.